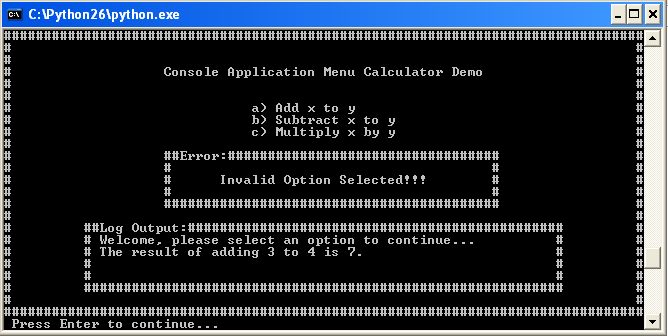
Well, it bothers me to build menus for every shell application that needs one.
So, I've written a module to handle that, like in the good old turbo pascal times. :)
Here it is, the module comments are pretty explainatory, I think, and the sample usage if run as script should enlighten the concept.
Use it, give comments, improvements, have fun...
Cheers and Happy coding